Source: FeedMagazine/Kraftfutter 9-10/2024
Authors: Prof. (i.R.) Dr. Josef Kamphues, Univ.-Dozent Dr. Leonhard Gruber
The new GfE (2023) Recommendations on the Energy and Nutrient Supply of Dairy Cows dedicate a full chapter to the complex interrelationships surrounding dry matter (DM) intake, offering both theoretical understanding and practical estimation values for ration planning under varying production conditions.
The traditional method—dividing the energy requirement by the energy density of feed—has been replaced by a predictive model based on influencing factors such as body weight (BW), milk performance, stage of lactation, and forage quality (especially digestibility). The approach is based on the work of Gruber et al. (2004) and reflects international reliability.
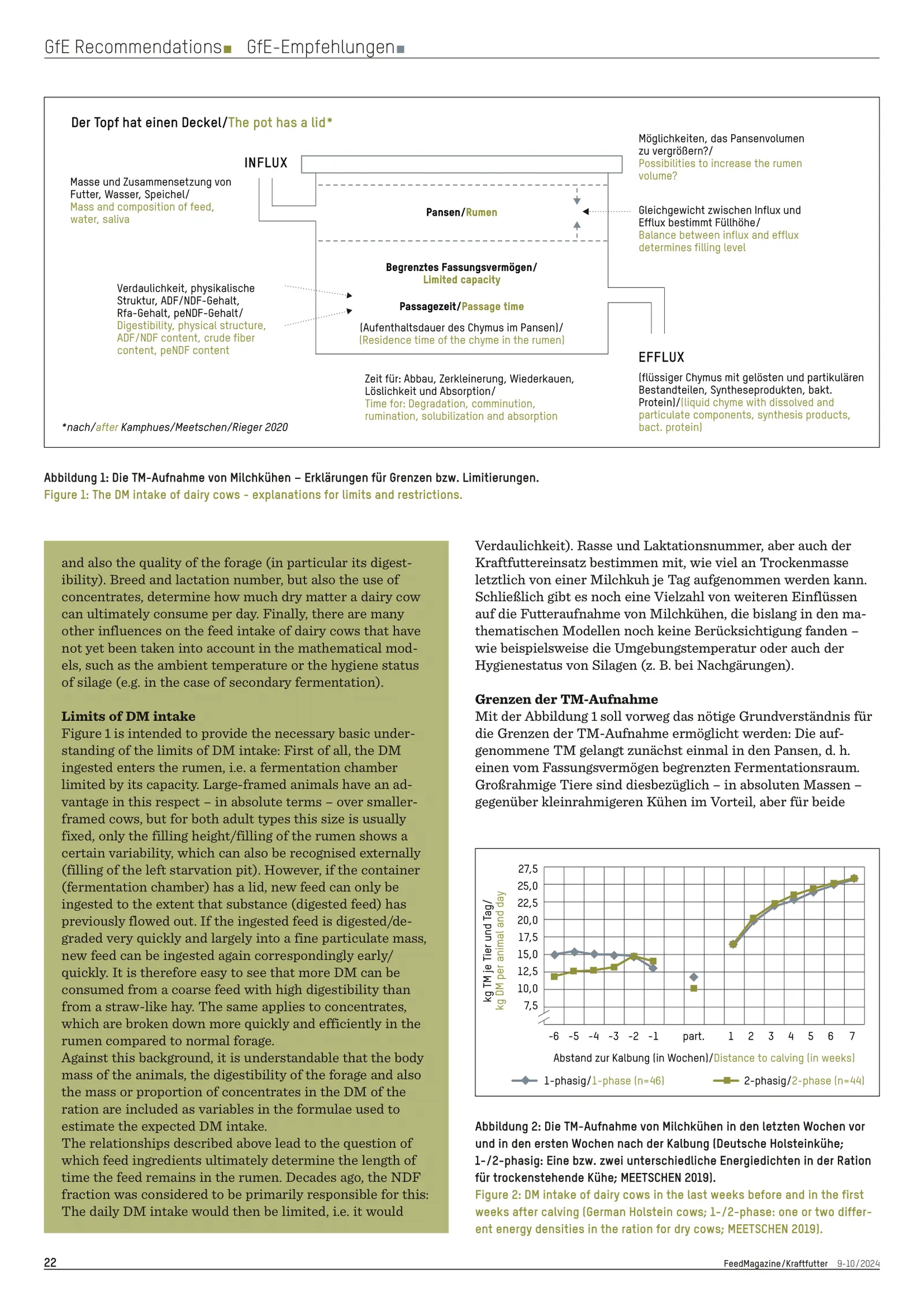
Breed, lactation number, and concentrate usage also impact DM intake, alongside external variables such as ambient temperature and silage hygiene. Physiological limits are explained through rumen capacity and feed retention time, influenced by the NDF (neutral detergent fiber) content. A threshold of 12.5 g NDF/kg BW/day is noted as limiting for DM intake. Highly digestible and finely chopped forage and concentrates can significantly increase intake, especially in high-yield phases.
DM intake is dynamic across the lactation curve: it decreases prepartum (1.6–1.8% of BW), increases rapidly postpartum, and peaks around the 100th day of lactation. After this, intake may exceed energy requirements, suggesting a potential for concentrate reduction and a shift to more forage-based feeding to avoid over-conditioning and associated risks like negative energy balance, ketosis, or fatty liver.
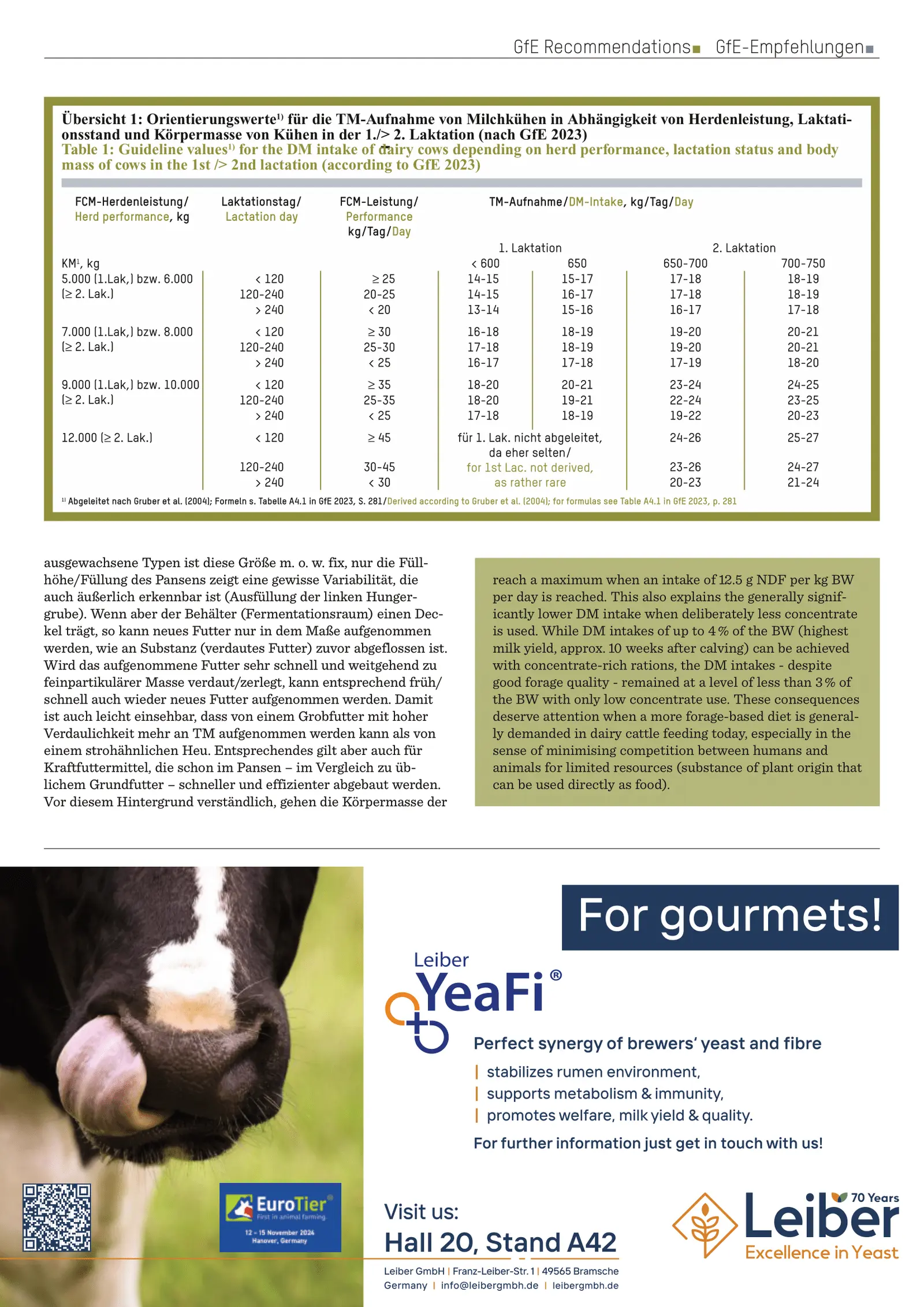
Orientation values for DM intake are provided across different lactation stages and performance levels, adjusted for forage quality and concentrate share. Intakes above 25 kg DM/day generally require significant concentrate use, which must be managed to maintain physiological rumen digestion and adequate physically effective NDF (peNDF).
Additional factors influencing DM intake include feeding technique (TMR, AGR, separate feeding), silage quality, and especially heat stress, which increases thermoregulatory strain. Other elements such as claw health, forage structure, and mixing homogeneity also play roles.
Lastly, drinking water availability is critical. A ratio of approximately 4:1 (litres of water per kg DM) is observed, especially with high milk yield and DM intake. Water restriction undermines both welfare and performance.
The text concludes that DM intake is a performance influenced by a range of animal, feed, environmental, and management factors. With the right data and conditions, it can be reliably estimated and optimized for herd health and productivity.
The New Regulations for Dairy Cow Feeding in HYBRIMIN Futter X
The latest GfE recommendations are integrated into HYBRIMIN Futter X. Contact our support team for more information.
 Croatian
Croatian Danish
Danish French
French German
German Greek
Greek Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Romanian
Romanian Russian
Russian Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish