Source: FeedMagazine/Kraftfutter 9-10/2024
Authors: Prof. Dr. Jürgen Zentek, Prof. Dr. Qendrim Zebeli, Prof. (i.R.) Dr. Josef Kamphues
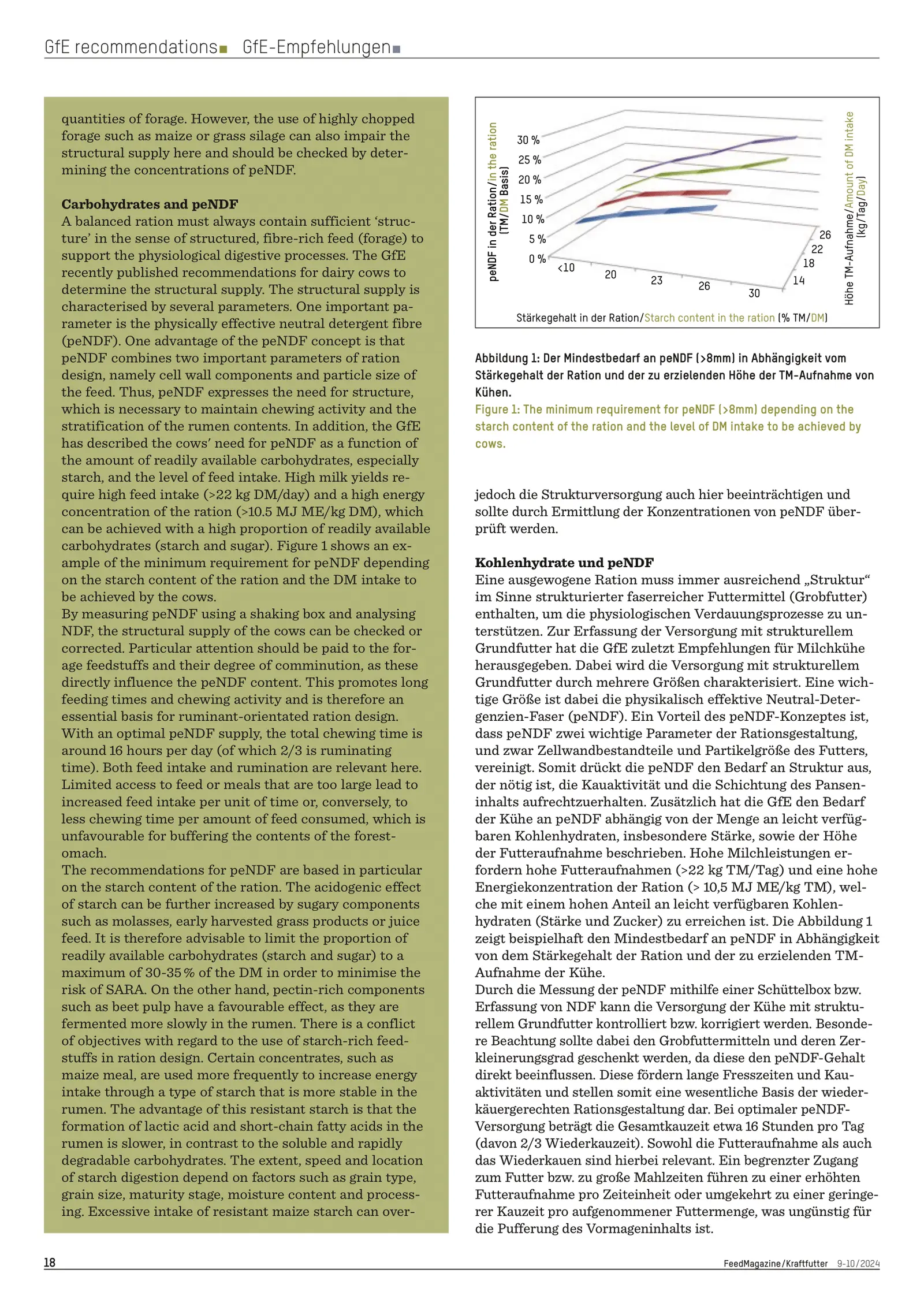
The article outlines updated recommendations for dairy cow nutrition, emphasizing the importance of ruminant-appropriate feeding to sustain health, welfare, and productivity. Central to this approach is the concept of physically effective neutral detergent fibre (peNDF), which integrates particle size and fibre content to support rumen function, chewing activity, and digestive health.
Modern dairy cows, due to genetic improvement and intensified feeding strategies, have high nutritional demands. Meeting these requires a careful balance between energy-dense rations and sufficient structural fibre. An inadequate supply of structural components increases the risk of subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA) and associated disorders such as displaced abomasum, mastitis, lameness, and fertility problems.
Nutritional management must be phase-specific:
- During the dry period and transit phase, cows should be prepared metabolically and physically for lactation through balanced rations with limited calcium and adequate structural fibre.
- In early and peak lactation, high energy requirements and limited feed intake necessitate a high metabolizable energy (ME) concentration. However, this must be balanced with adequate peNDF to avoid ruminal disorders.
- In mid to late lactation, ration formulation becomes easier, but the structure must still be monitored, especially when using finely chopped forages.
Carbohydrate composition and fermentation rate play crucial roles.
Fat supplementation can increase ration energy density, particularly for high-yielding cows, but total crude fat should not exceed ~6% of DM. Rumen-protected fats are better tolerated than free oils.
For cows exceeding 10,000 kg milk per lactation, maintaining epithelial barrier integrity and microbiota health is critical. Nutritional stress, contaminated feed (e.g., with mycotoxins), and acidotic conditions should be avoided. Buffer substances like sodium bicarbonate may help mitigate risks but do not substitute for proper ration design.
Conclusion:
A species-appropriate feeding strategy, rooted in concepts like peNDF and adjusted to each lactation phase, is essential for sustaining cow health and productivity. Continuous refinement based on new scientific insights is vital for optimal herd management.
The New Regulations for Dairy Cow Feeding in HYBRIMIN Futter X
The latest GfE recommendations are integrated into HYBRIMIN Futter X. Contact our support team for more information.
 Croatian
Croatian Danish
Danish French
French German
German Greek
Greek Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Romanian
Romanian Russian
Russian Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish